Colonization Resistance

Coming Soon

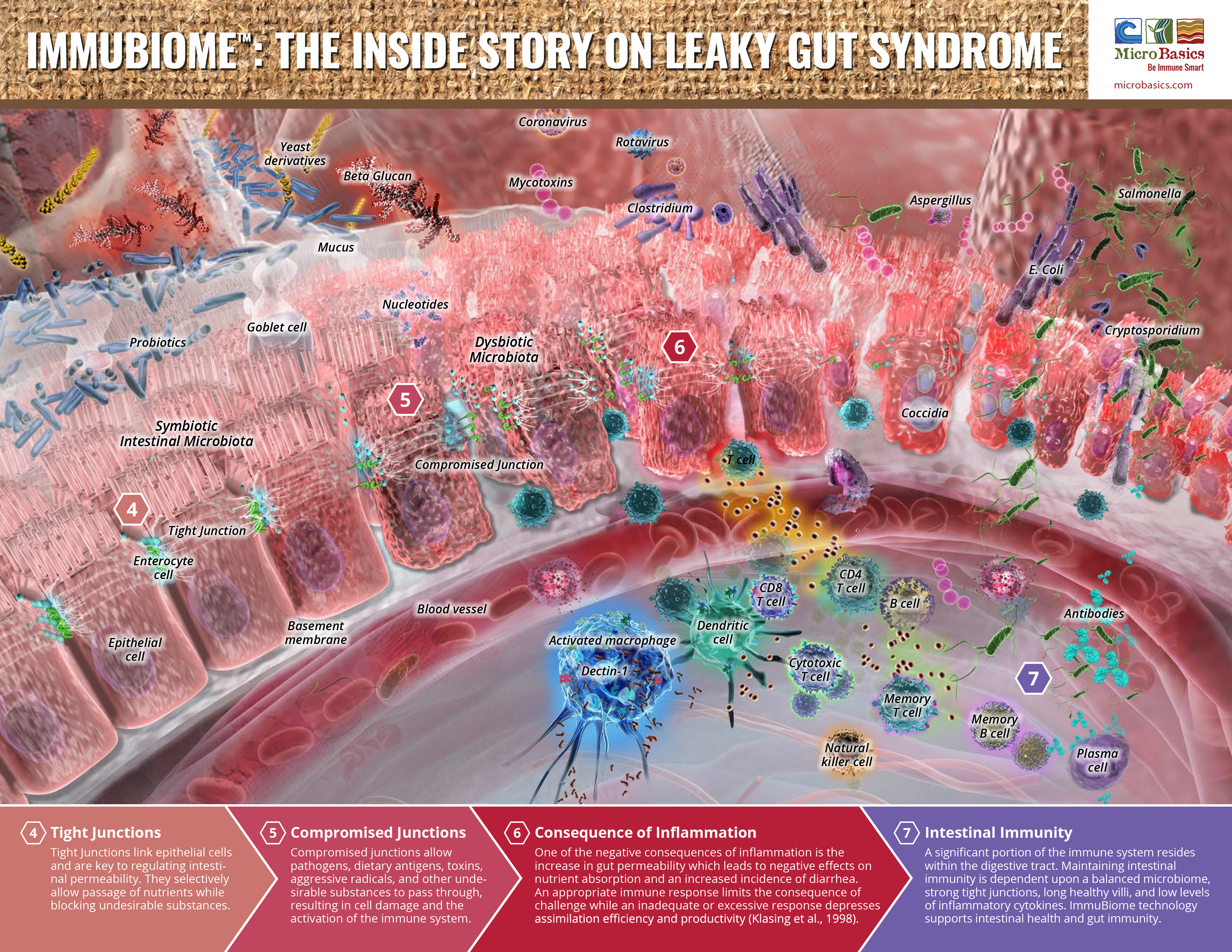
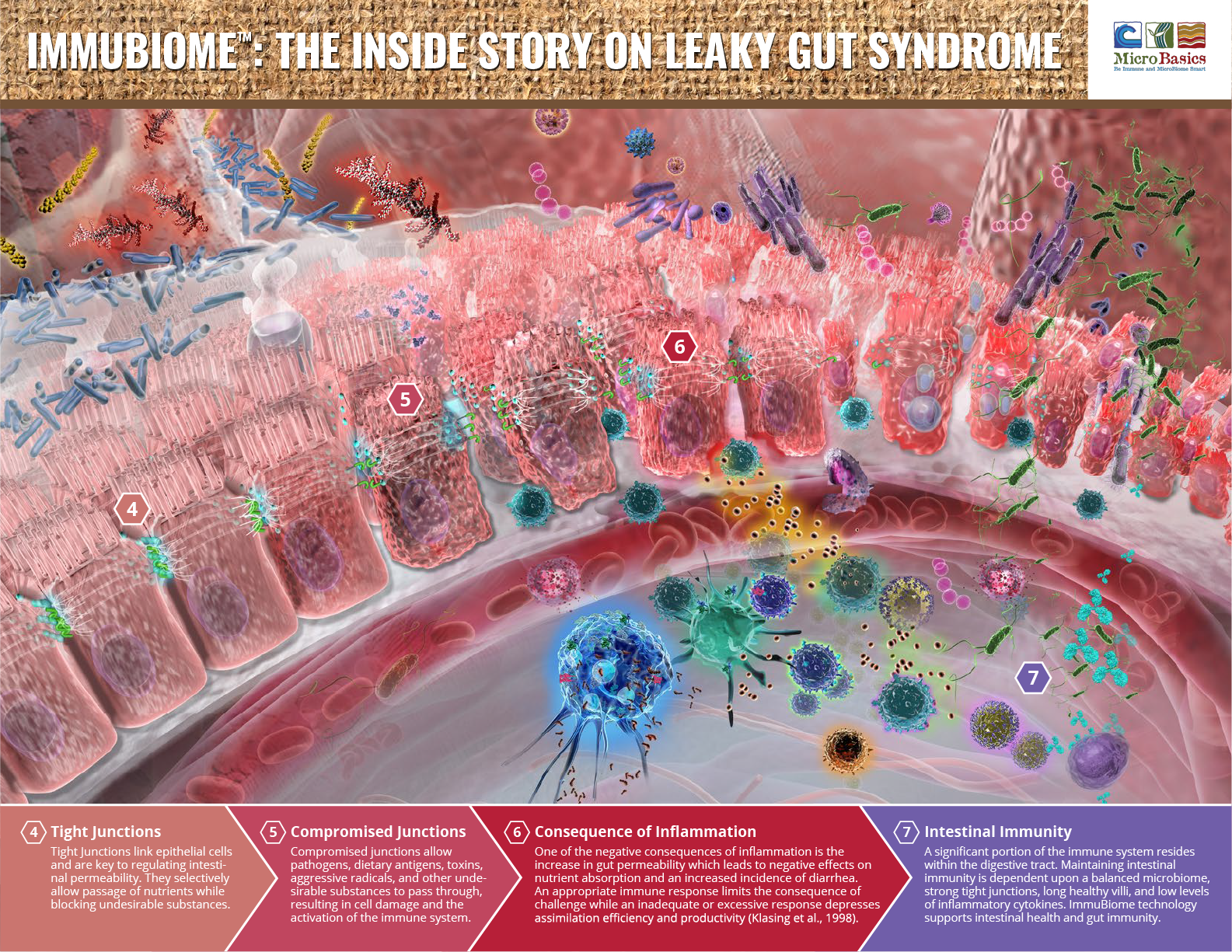
Beta glucans are a class of polysaccharides found widespread in nature and may be derived from a variety of sources. Many beta glucans derived from fungi have the ability to behave as immunomodulators. In this illustration beta glucan is activating a macrophage, triggering a cascade of immune events to occur.

Mucus is the slippery secretion produced by mucus cells (i.e. goblet cells) among the epithelial lining of the intestine. Mucus serves to protect and lubricate the bowel.

Goblet cells are specialized cells which reside throughout the length of the small and large intestine and are responsible for the production of protective mucus.

Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can colonize the intestinal tract. Probiotics compete with the “bad” bacterial inhabitants for space along the intestinal wall.

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Epithelial cells are cells arranged in one or more layers to form epithelial tissues. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of blood vessels and organs throughout the body.

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Coming Soon

Coronavirus is a common virus which primarily infects the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract of mammals and birds.

Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites produced by many species of fungi. Mycotoxins can contaminate feedstuffs and upon ingestion, may severely compromise animal health.

Clostridium are anaerobic rod-shaped, gram positive bacteria of a large genus which includes many pathogenic species. Clostridium perfringens has been implicated in the development of Hemorrhagic Bowel Syndrome (HBS).

An activated macrophage is one that has been ‘turned on’ and is in an active metabolic state.

Dectin-1 is a receptor for -glucans expressed on phagocytic leukocytes.

Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells of the immune system. DCs act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems, processing antigen material and presenting it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system.

Coming Soon

A CD4+ T cells are T cells expressing the CD4 co-receptor. CD4 co-receptor assists the T cell receptor in communicating with antigen presenting cells.

B cells or B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that function in the humoral immunity. B cells multiply and mature into antibody producing plasma cells.

Cytotoxic T cells are a subset of T cells that have the ability to directly kill infected and damaged cells. Cytotoxic T cells usually express the CD8 co-receptor.

Memory T cells are T cells that have previously encountered and overcome an infection. Memory T cells are capable of ‘remembering’ the most effective strategy employed, enabling them to fight off re-occurrence of the same disease.

Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type capable of ‘remembering’ previously encountered pathogens for faster antibody production in future infections.

Natural killer cells (NK cells) are a type of white blood cell able to kill infected and damaged cells without reliance upon antigen recognition.

Plasma cells are fully differentiated B cells that secrete large volumes of antibodies.

Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are Y shaped protein molecules produced by the immune system in response to foreign antigen such as viruses and bacteria. Antibodies stick to specific antigens, marking them for destruction.

Coming Soon

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of a few hundred mold species. Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus are two species known to produce Aflatoxin.

Escherichia coli
(E.coli) is a rod-shaped, gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium and is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. However, some pathogenic strains such as K99 and O157:H7 can cause severe intestinal infection.

Salmonella are rod-shaped, gram-negative bacteria that can adhere to the intestinal tract resulting in severe diarrhea and potentially life-threatening dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.

Cryptosporidium is a microscopic parasite that can cause diarrheal disease cryptosporidiosis, commonly known as “Crypto.”